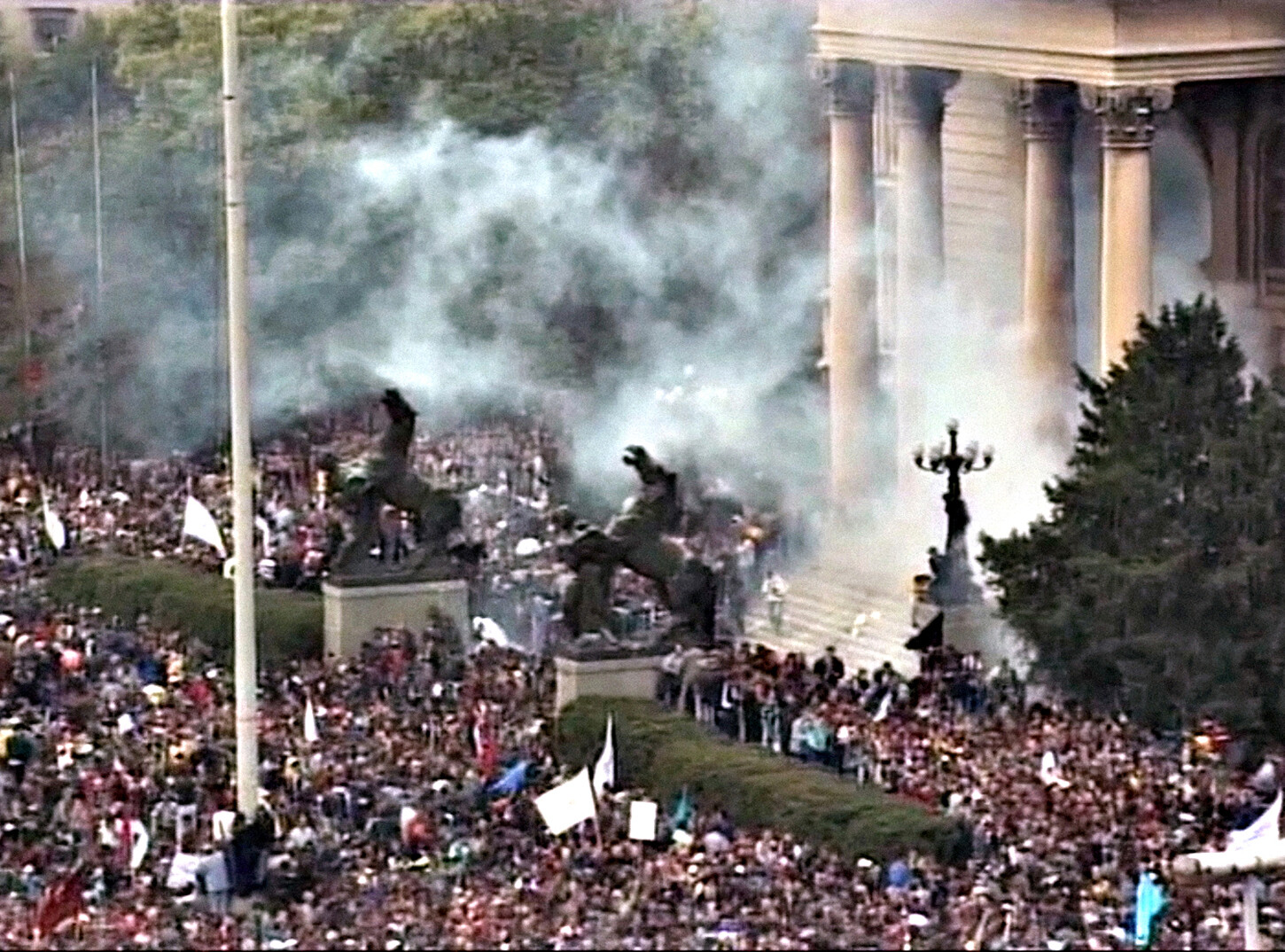Felicity D. Scott, “An Eye Half Open Only to Architecture”
Part Three
Screening: On trash collectors and Michael Jackson impersonators
In The Shock Doctrine, Naomi Klein describes how when a crisis happens, companies infiltrate society, and the government imposes new rules or cuts. It’s sometimes more possible in the art sector to see individuals, groups, and collectives using these moments to infiltrate the structure that is in crisis or that claims the crisis.
Contested Representations: Making Images from Elsewhere
Contested Representations: Making Images from Elsewhere
With Irmgard Emmelhainz, Olivier Hadouchi, Khaled Saghieh, Stefan Tarnowski
How to create a community within the arena of biopower without killing off the individual? How to create a collective, and not some zombifying crowdedness, while living in a democracy that is currently being transformed into a discursive category debated at conferences? How to create a body, a Hamletian body that will stand against and redefine the imposed lie of capitalism, of injustice?
With the industrial revolution, curing and caring for oneself took an individualist turn: it became a private affair for the privileged. Self-care was turned into a sign of cultural sophistication for the Western imperialist class.
Nothing makes more sense today than to revamp the social imaginary of our collective body. That body is in danger. It is under attack by other species. It is wounded. Its immunity has to be built. It has to be taken care of. It should heal. And it can only heal collectively. At the same time, nothing seems less probable.
The singular image of the blue marble is now divided into different worlds which form a constellation that has nothing to do with celestial harmony. We are caught within it, where for each decision we must make, the gravitational attractions of the different configurations of earth make one’s head rotate as if on a merry-go-round. The model for describing this condition is not just some new form of dialectic (implying only two poles), but rather a configuration with a multiplicity of polarities.
Care and its politics have been a subject of concern to the art world, made all the more urgent by the global pandemic. But is it a real concern that can lead to changes in the way we operate in our institutions and working relationships, or is it merely surface level? How can care, if studied care-fully, provide solutions to the various problems that art institutions and art workers face? How is it that contemporary art institutions are keen—and comfortable—to talk about care when they have been so care-less?